2415. Reverse Odd Levels of Binary Tree
2415. Reverse Odd Levels of Binary Tree
[Problem]
Tree Depth-First Search Breadth-First Search Binary Tree
Intuition
- We only need to reverse the values at odd levels while maintaining the tree structure.
Approach
1. BFS (Breadth-First Search)
- Use BFS to process the tree level by level.
- Track the level number (starting from 0 for the root).
- If the current level is odd(
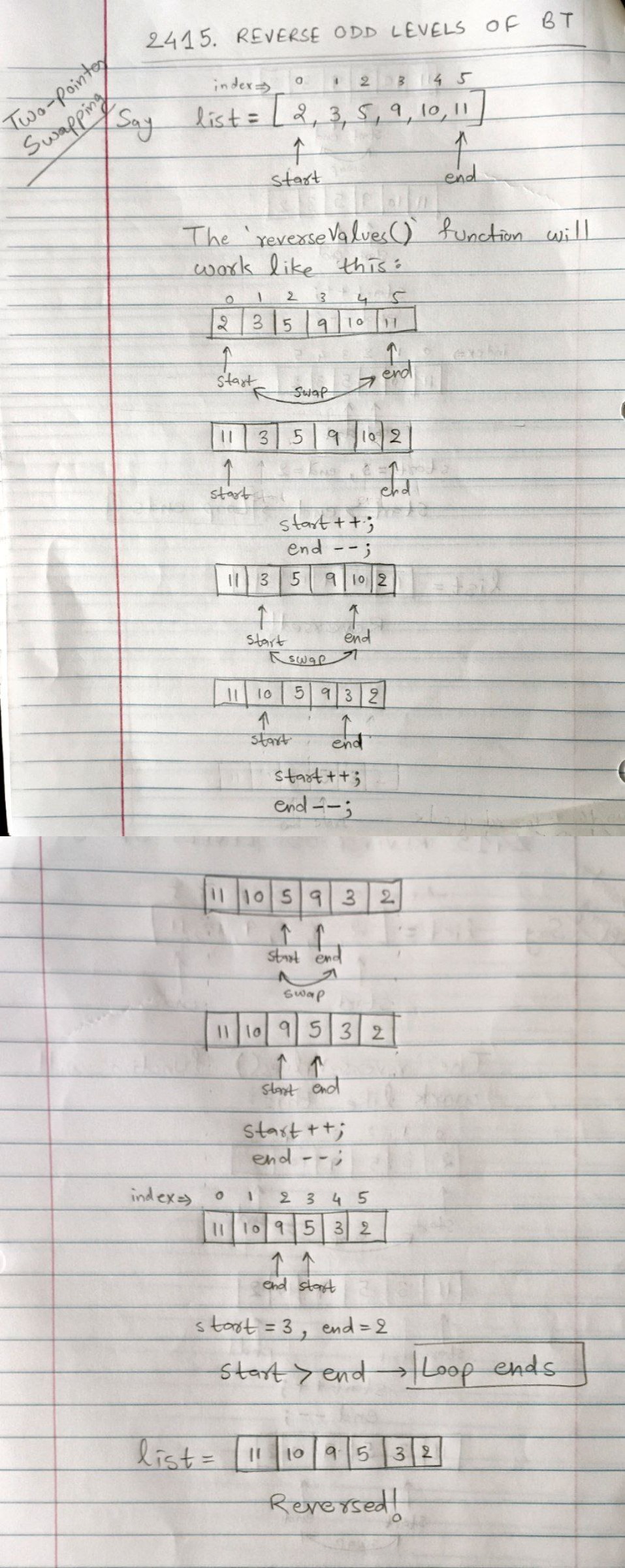
level % 2 == 1), reverse the values of nodes at that level.- To reverse the node values we can use two-pointer technique.
- Keep
startandendpointers at extremes of the list. - Keep swapping the values
while(start < end)! - Refer this:
- Code for this part:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void reverseValues(List<TreeNode> currentLevel){
int start = 0, end = currentLevel.size() - 1;
while (start < end) {
// swap values
int tmp = currentLevel.get(left).val;
currentLevel.get(start).val = currentLevel.get(end).val;
currentLevel.get(end).val = tmp;
// increment start, decrement end
start++;
end--;
}
}
- Use a
queueto traverse the tree level-by-level. - Store nodes at each level in a temporary list.
- If the level is odd, reverse the values in the list (two-pointer technique).
- Continue traversing until all levels are explored.
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public TreeNode reverseBFS(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
int lvl = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// no. of elements in current level
int lvlSize = q.size();
// storing elements of the current level in a list
List<TreeNode> currentLevel = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < lvlSize; i++) {
TreeNode current = q.poll();
currentLevel.add(current);
// add next level nodes in the queue
if (current.left != null) q.add(current.left);
if (current.right != null) q.add(current.right);
}
// Reverse values at odd levels
if (lvl % 2 == 1) {
reverseValues(currentLevel);
}
lvl++;
}
return root;
}
// remember, we only reverse the values not the nodes itself, hence the tree structure is maintained
public void reverseValues(List<TreeNode> currentLevel){
int start = 0, end = currentLevel.size() - 1;
while (start < end) {
int tmp = currentLevel.get(left).val;
currentLevel.get(start).val = currentLevel.get(end).val;
currentLevel.get(end).val = tmp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
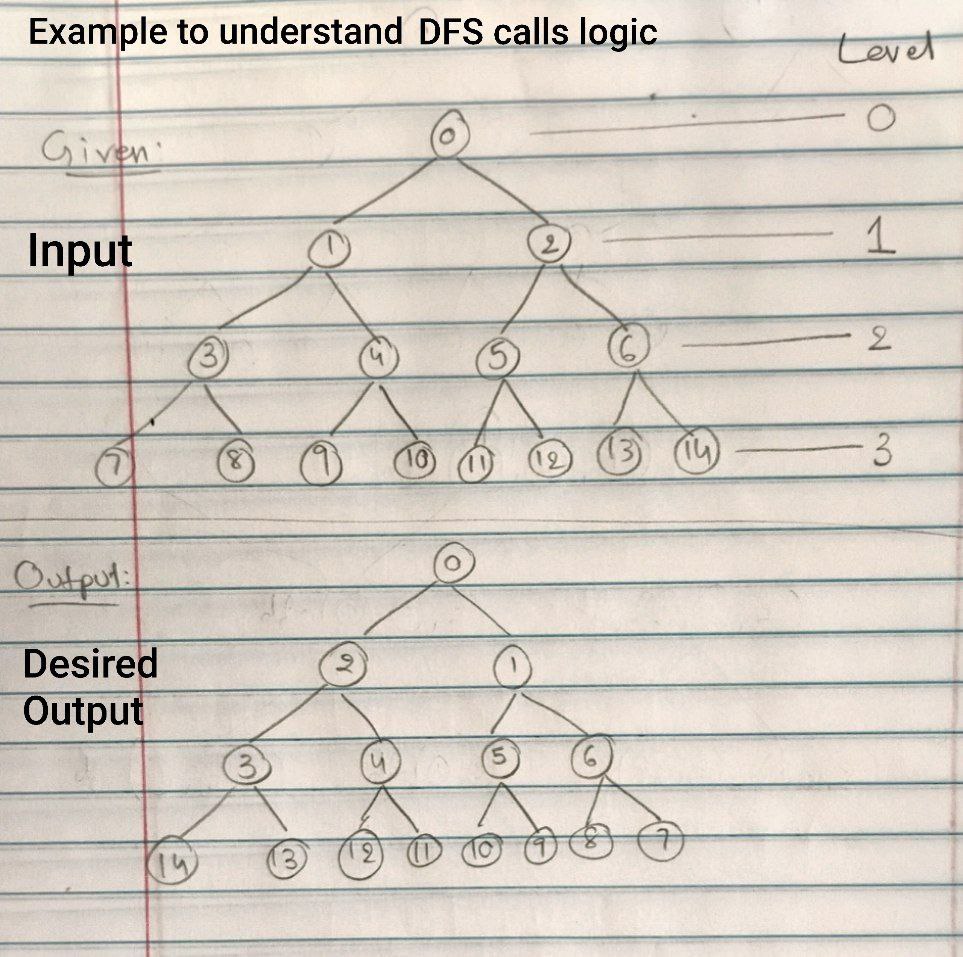
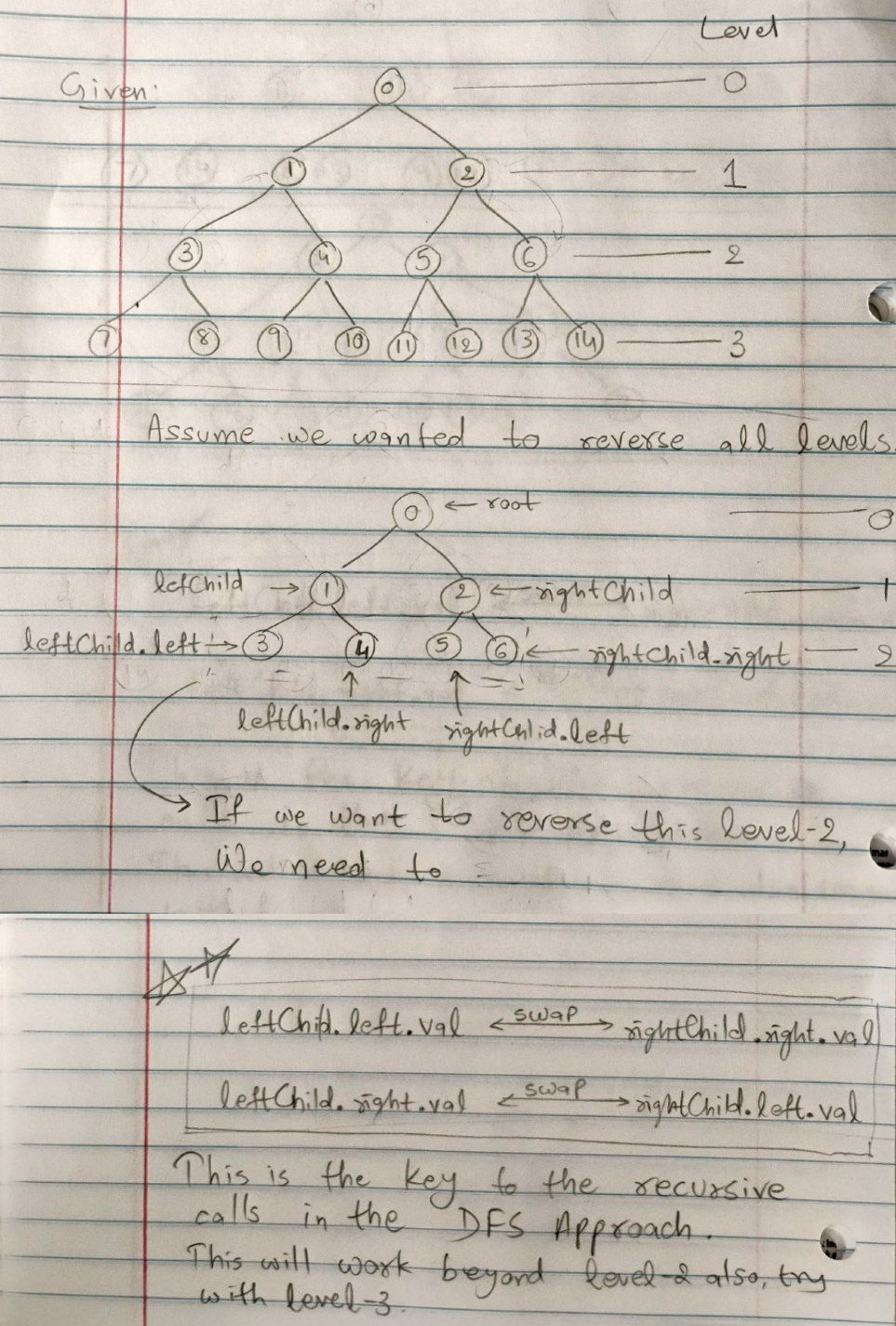
2. DFS (Depth-First Search)
For any two symmetric nodes at the same level, the left node and the right node can have their values swapped.
- Start with the root’s left and right children.
- At each recursive call:
- If the current level is odd, swap the values of the two symmetric nodes.
- Recursively process:
- Left child’s left subtree with the right child’s right subtree.
- Left child’s right subtree with the right child’s left subtree.
- WHY?
Stop the recursion when either of the
leftChildorrightChildisnull.Note: We only reverse nodes values at odd levels which keeps the tree structure maintained.
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
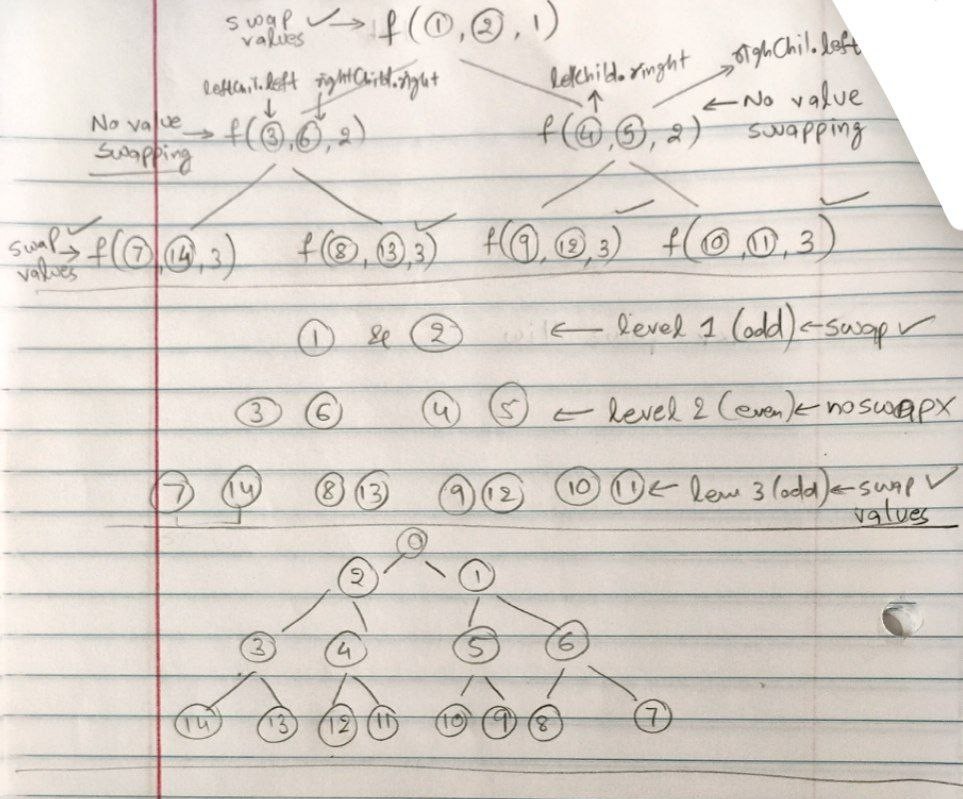
public void reverseDFS(TreeNode leftChild, TreeNode rightChild, int lvl) {
if (leftChild == null || rightChild == null) {
return; // Base case: stop when no more nodes to process
}
if (lvl % 2 == 1) { // If the current level is odd, swap the values
int tmp = leftChild.val;
leftChild.val = rightChild.val;
rightChild.val = tmp;
}
// Recurse for next level
reverseDFS(leftChild.left, rightChild.right, lvl + 1); // Outer pair
reverseDFS(leftChild.right, rightChild.left, lvl + 1); // Inner pair
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.