3203. Find Minimum Diameter after Merging Two Trees
3203. Find Minimum Diameter after Merging Two Trees
[Problem]
Tree Depth-First Search Breadth-First Search Graph
Tip: Solve Leetcode 1245. Tree Diameter (Unlocked) before attempting this question to gain a foundational understanding.
Intuition
Note: This problem requires understanding tree diameters, which are the longest paths in a tree (undirected acyclic graph).
To minimize the merged diameter:
- Find the diameters of the two trees.
- Connect nodes near the midpoint of each diameter to reduce the overall length effectively.
Approach
1. Calculate the Diameter of Each Tree
- Use the two-pass DFS method:
- Perform DFS from an arbitrary node to find the farthest node (
farthest1). - From
farthest1, perform another DFS to find the farthest node (farthest2). - The distance between
farthest1andfarthest2is the tree’s diameter.
- Perform DFS from an arbitrary node to find the farthest node (
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public int findDiameter(List<List<Integer>> adjList, int totalNodes) {
visited = new boolean[totalNodes];
farthestNode = adjList.get(0).get(0);
maxDiameter = 0;
dfs(farthestNode, 0, adjList);
visited = new boolean[totalNodes];
dfs(farthestNode, 0, adjList);
return maxDiameter;
}
2. Merge the Trees
- Calculate the diameters
d1andd2of tree1 and tree2. - Connect the middle nodes of both trees to minimize the new diameter:
1
2
3
int r1 = (int) Math.ceil((float) d1 / 2);
int r2 = (int) Math.ceil((float) d2 / 2);
int mergedDiameter = Math.max(d1, d2, r1 + 1 + r2);
3. Determine the Minimum Diameter
- The result is the maximum of the following:
1
result = Math.max(d1, d2, r1 + 1 + r2);
Warning: If both trees have only one node, handle the edge case where the merged diameter is
1.
Merging Procedure (Example)
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Tree1 and Tree2 | 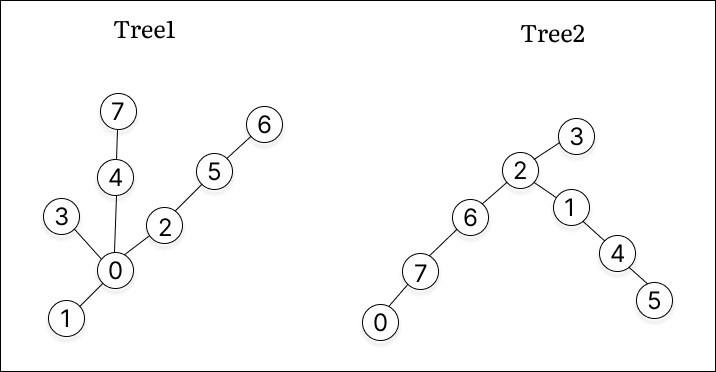 |
| 2. Compute Diameters | 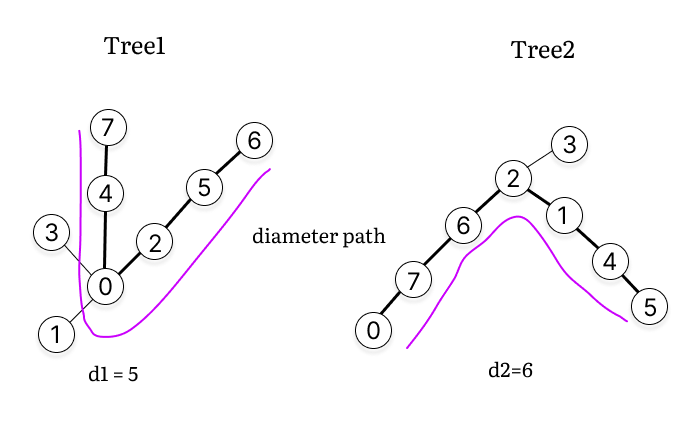 |
| 3. Find Middle Nodes |  |
| 4. Merge Trees |  |
| 5. Final Merged Tree | 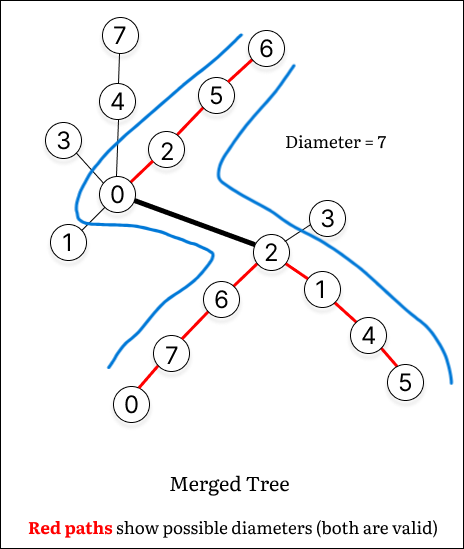 |
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:O(n + m)
nandmare the no. of nodes in the two trees.- DFS is performed on each tree to calculate the diameter, and merging involves constant-time operations.
- Space Complexity:O(n + m)
O(n + m)for storing the adjacency lists of the two trees and stack space of recursive DFS.
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
class Solution {
private boolean[] visited;
private int maxDiameter;
private int farthestNode;
public int minimumDiameterAfterMerge(int[][] tree1Edges, int[][] tree2Edges) {
return calculateMinimumDiameter(tree1Edges, tree2Edges);
}
public int calculateMinimumDiameter(int[][] tree1Edges, int[][] tree2Edges) {
int n = tree1Edges.length + 1; // no. of nodes in tree1
int m = tree2Edges.length + 1; // no. of nodes in tree2
List<List<Integer>> adj1 = buildAdjList(tree1Edges, n); // adjacency list tree1
List<List<Integer>> adj2 = buildAdjList(tree2Edges, m);
int d1 = n == 1 ? 0 : findDiameter(adj1, n); // tree1 diameter
int d2 = m == 1 ? 0 : findDiameter(adj2, m);
// if both trees have only one node, the merged tree has a diameter of `1`
if (d1 == 0 && d2 == 0) {
return 1;
}
// special case where one tree has diameter `1` and the other has diameter `0`
if ((d1 == 1 && d2 == 0) || (d1 == 0 && d2 == 1)) {
return Math.max(d1, d2) + 1;
}
// calculate the new diameter of the merged tree
// you can also write `r1 = (d1+1)/2`
int r1 = (int) Math.ceil((float) d1 / 2); // middle of d1 (r => radius, just for naming convention)
int r2 = (int) Math.ceil((float) d2 / 2);
// mergedDiameter is MAX(d1, d2, r1 + 1 + r2)
int mergedDiameter = Math.max(d1, d2);
mergedDiameter = Math.max(mergedDiameter, r1 + 1 + r2);
return mergedDiameter;
}
// build adjacency list
public List<List<Integer>> buildAdjList(int[][] edges, int totalNodes) {
List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>(totalNodes);
for (int i = 0; i < totalNodes; i++) {
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
adjList.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
adjList.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
return adjList;
}
// find the diameter of a tree using two-pass DFS
public int findDiameter(List<List<Integer>> adjList, int totalNodes) {
visited = new boolean[totalNodes];
farthestNode = adjList.get(0).get(0); // arbitrary starting point
maxDiameter = 0;
// first DFS to find one endpoint of the diameter
dfs(farthestNode, 0, adjList);
// reset visited array and perform DFS from the farthest node to calculate the diameter
visited = new boolean[totalNodes];
dfs(farthestNode, 0, adjList);
return maxDiameter;
}
// DFS to find the farthest node and track the maximum distance
public void dfs(int node, int distance, List<List<Integer>> adjList) {
if (visited[node]) {
return;
}
visited[node] = true;
if (maxDiameter < distance) {
// keep updating the max distance and the farthest node
maxDiameter = distance;
farthestNode = node;
}
for (int neighbor : adjList.get(node)) {
dfs(neighbor, distance + 1, adjList);
}
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.
