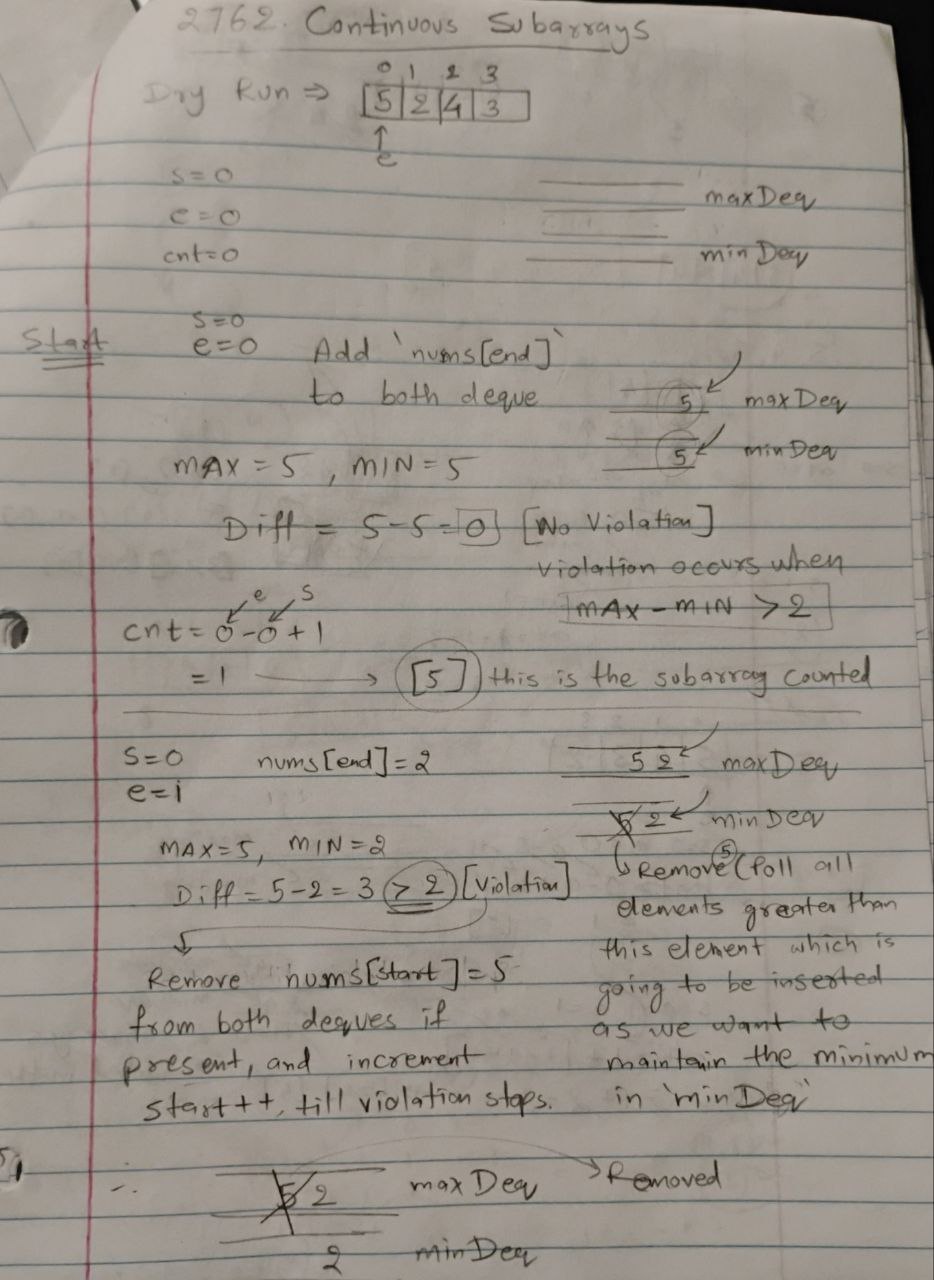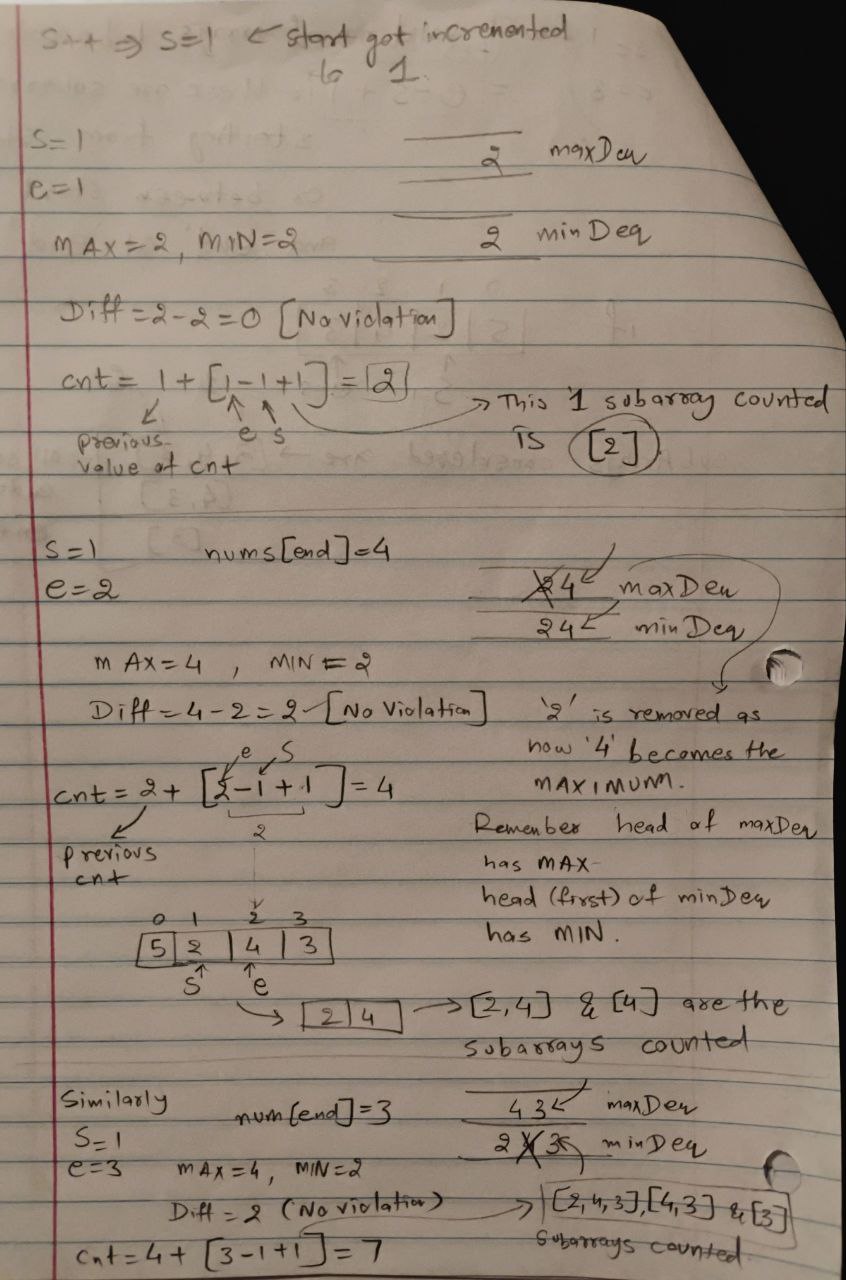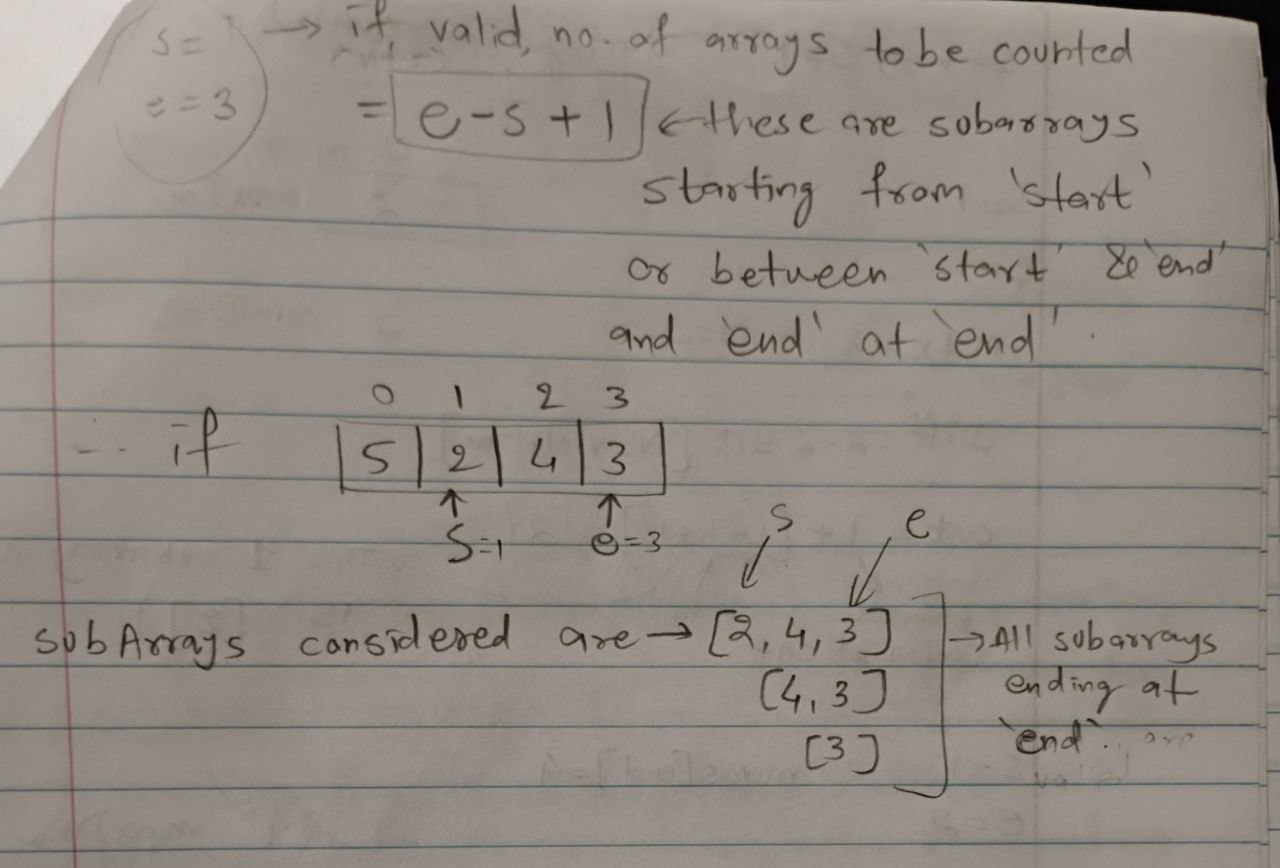2762. Continuous Subarrays
2762. Continuous Subarrays
[Problem]
Array Queue Sliding Window Heap(Priority Queue) Ordered Set Monotonic Queue
Approach
1. Brute-Force
- The obvious brute-force approach is simple, check all subarrays if they satisfy the condition
- But total subarrays in an
n-sizedarray aren*(n+1)/2, which is order ofO(n^2). - Moreover you iterate through each of them to find whether they are continuous or not.
- This brings the time complexity in order of
O(n^3), which is exactly why TLE (Time Limit Exceeded) occurs in leetcode (2129/2135 case).
Here’s the code for the brute-force approach:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// Not preferable O(n^3) solution
class Solution {
public long continuousSubarrays(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
long count = 0;
// this approach will take O(n^3) time, hence TLE will occur
int start = 0;
for(int end = 0; end < n; end++){
while(!isCont(nums, start, end)){
start++;
}
count += end - start + 1; // count total valid subarrays for given `start` and `end` pointers
}
return count;
}
// function to iterate thorugh a subarray to check if it is continuous or not
public boolean isCont(int[] nums, int start, int end){
for(int i = start; i <= end; i++){
for(int j = i + 1; j <= end; j++){
int diff = Math.abs(nums[i] - nums[j]);
if(diff > 2){
return false; // condition for continuous array violated
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
2. A better-approach: Sliding Window with Deque
We utilize a sliding window technique with the help of two deques:
maxDeq: Maintains the maximum values in the current sliding window.minDeq: Maintains the minimum values in the current sliding window.
Steps:
- Iterate with a sliding window (
endpointer):- Expand the window by adding
nums[end]to bothmaxDeqandminDeq.
- Expand the window by adding
- Maintain Monotonic Deques:
maxDeq: Ensure elements are in decreasing order by removing smaller elements from the back.minDeq: Ensure elements are in increasing order by removing larger elements from the back.
- Validate the Window:
- The difference between the maximum (
maxDeq.peekFirst()) and minimum (minDeq.peekFirst()) values should not exceed2. - If the condition is violated, shrink the window by incrementing the
startpointer and removing the corresponding values from the deques.
- The difference between the maximum (
- Count Valid Subarrays:
- For each valid window, the number of subarrays ending at index
endis given by:end - start + 1
- For each valid window, the number of subarrays ending at index
- Return Total Count:
- Add
countfrom all valid windows.
- Add
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Each element is added and removed from the deques at most once, hence
O(n)
- Each element is added and removed from the deques at most once, hence
- Space Complexity:
- The two deques require
O(n)space in the worst case.
- The two deques require
Reference Images
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
class Solution {
public long continuousSubarrays(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
long cnt = 0;
// Two deques to maintain the maximum and minimum values in the current window
Deque<Integer> maxDeq = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<Integer> minDeq = new LinkedList<>();
int start = 0;
// Iterate through the array with the `end` pointer
for(int end = 0; end < n; end++){
// Maintain decreasing order in maxDeq
while(!maxDeq.isEmpty() && nums[end] > maxDeq.peekLast()){
maxDeq.pollLast();
}
// Maintain increasing order in minDeq
while(!minDeq.isEmpty() && nums[end] < minDeq.peekLast()){
minDeq.pollLast();
}
// Add current element to both deques
maxDeq.offerLast(nums[end]);
minDeq.offerLast(nums[end]);
// while the continuous array conditions are violated
// keep shrinking the window from left, i.e. increment `start`
while(maxDeq.peekFirst() - minDeq.peekFirst() > 2){
if(nums[start] == maxDeq.peekFirst()){
maxDeq.pollFirst();
}
if(nums[start] == minDeq.peekFirst()){
minDeq.pollFirst();
}
start++;
}
// for valid subarray, count all possible subarrays
// these are all subarrays ending at `end` and starting between `start` and `end` are valid
cnt += end - start + 1;
}
return cnt;
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.